With over 3.5 billion searches every day, it is no surprise that Google (along with other search engines) can bring a wealth of valuable visitors to any website.
So, whether you run an ecommerce store, a service business website, a media site, or you just want to grow your blog – making your website more appealing to search engines is well worth your while.
From conducting extensive keyword research to posting regular blog content, there are countless ways to optimise your website in order to improve your rankings on Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs).
However, many website owners fail to get the basic ‘behind-the-scenes’ aspects, such as meta tags, right.
This can often lead to all the efforts made to publish great content and design stunning, user-friendly sites being largely a waste of time.
Taking the time to get the right meta tag processes and best practices in place will help search engines identify just how fantastic your website is and will give them everything they need to serve your content to the most relevant (and often most profitable) people.
In this guide, we are going to walk you through:
- What are meta tags
- Why (some) meta tags are so important to Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
- Which meta tags you should be concerned about when it comes to SEO
- How to apply those meta tags to your website
- Best practices to apply meta tags to your website
Ready to find out how to drastically improve your chances of reaching the coveted ‘first page’ of Google?
Then read on…
What are Meta Tags?
Whether you are just getting started with SEO, or you are a seasoned professional, you have probably heard the term ‘Meta Tags’ being mentioned a lot.
These are now most commonly mentioned in negative terms, such as how some meta tags are a waste of time when it comes to search engine optimisation.
Yet in reality, meta tags are still a powerful SEO tool – but only if you take the time to understand how they work and how to apply them properly to your website.
This guide will tell you everything you need to know about meta tags and how to add them to your website successfully.
But what actually are meta tags?
‘Meta’ refers to ‘metadata’ – which is the type of data provided by these tags.
Just to complicate things, this means that meta tags can be described as ‘data about the data that is on any given webpage’ – but don’t worry, we will explain this much better…
Meta tags can be defined as small snippets of text that describe a web page’s content.
However, these snippets of text aren’t physically visible on the page. Instead, meta tags are only visible on the page’s source code (HTML).

Here’s how to view meta tags of any page.
- On your browser, go to the URL you wish to see meta tags for.
- Right click and then click “View Page Source”. (CTRL + U)
- A new tab will open with the source code of the page.
- Search the page with CTRL + F
- Search for the word “meta”
- All meta tags will generally be clubbed in the head of the page.
This approach allows web browsers and search engines such as Google to understand what the webpage is all about, without the need for messy keywords and descriptions to be plastered all over the visible part of the webpage.
This ensures that those who own and create websites can focus on delivering the best possible user experience, whilst still benefiting from the search engine boosting power of keywords and descriptions.
Meta tags are different from the tags you would typically see on a piece of content such as a blog post.
These visible on-page tags are usually used to help connect readers with other content which is relevant or may be helpful. For example, a visible tag at the top of a blog post about fashion is likely to link the reader through to lots of other useful blog posts about the same topic.
On the other hand, meta tags only exist in the HTML of the page (most commonly in the <head> of the page).
This means meta tags are only visible when the page source is viewed.
Meta tags also offer search engines insight into how your web page should be displayed on their results pages.
For example, the <title> and <description> elements of your HTML will tell search engines which title and description to display – this can actually be different to the title or any description used on the webpage.
Why do Meta Tags Matter?
So, we have offered you a detailed insight into what meta tags are…but why do they actually matter?
After all, if your readers can’t see them, are they going to make their experience any better?
Well – yes.
Meta tags are so important because it makes it clear and obvious to search engines and browsers what your website content is all about.
This ensures that readers who find their way onto your content via search engines are actually finding the information they are looking for.
Without meta tags, it can be more tricky for search engines to define the key information your webpage contains. In turn, this makes it tricky for them to know who best to serve your page to when analyzing search inquiries.
This can lead to irrelevant traffic finding its way to your site.
There is little value in gaining this irrelevant traffic as it will only usually serve to increase your bounce rate and decrease your session times.
It is clear that meta tags matter. So, you may be wondering why they so often get mentioned in a negative way.
This is because not all meta tags are created equal.
Some benefit your SEO efforts, whilst others waste your time.
Here is former Google head of Webspam Matt Cutts on how much time you should spend on meta tags.
The rest of this guide will be dedicated to differentiating between the two and offering you tips and guidance on how to apply best those that really make a difference.
Meta Tags: Which Ones Matter?
Want to know which meta tags actually matter when it comes to SEO? Here they are:
- Meta Titles
- Meta Descriptions
- Meta Robots
- Meta Refresh Direct
- Meta Charset
- Meta Viewports
Below, we will go into more detail on each of these meta tags which as what they are, why they are important and best practices in applying them to your website.
Meta Titles
Your meta title is by far one of the most important meta tags you will deal with when it comes to webpage content.
Unlike a page title or blog post title, which typically sits at the top of your webpage, your meta title is the title that searchers will see linking through to your content in their search results.
However, unless you stipulate your meta title with a <title> tag, search engines such as Google are likely to pick up the title you have used on your page – even if this isn’t the best option for highlighting the content on that page.
Why is writing a great meta title so important?
“Title links are critical to giving users a quick insight into the content of a result and why it’s relevant to their query. It’s often the primary piece of information people use to decide which result to click on, so it’s important to use high-quality title text on your web pages.”
Or in other words – your meta title is probably the most important words you will ever write about that specific piece of content.
This is because it is likely to be the first thing that people read in search results and therefore it is the information they will use to determine whether your website is ‘click worthy’.
You can consider your title tag as the first opportunity you get to sell searchers on your website – so you want to get it right.
Meta Titles Common Mistakes
There are many common mistakes with title tags with the following being the most common
- Meta title length. Google advises to avoid long titles while also making sure they are descriptive and concise.
- Missing meta titles. Often main pages of a website are missing meta titles which leads Google to use something else on the page as a title.
- Multiple title tags. If you have multiple plugins for SEO or have manually injected your page with <title> tags, double check how many times they appear. Multiple title tags can confuse Google.
- Duplicate titles across pages. Often multiple pages share the same meta title. This is not the best practice.
- Meta title too verbose or long. Webmasters will often use a very long and a verbose title for the meta title. This makes Google trim the title or often ignore it completely.
Meta Title Best Practices
It is clear that your meta title is important, but how do you make sure you create the best one possible? Here are some tips:
Do…
- Limit your title to 55 characters
- Write a unique title for every page
- Use your primary keyword or keyphrase prominently
- Make sure it’s click-worthy and interesting
- Describe the value you are offering
- Match search intent
Don’t…
- Forget to write a meta title
- Be generic
- Exceed 60 characters
- Use too many keywords or repeat your keywords
- Use a meta title that isn’t relevant to the page
Meta Descriptions
If your meta title is the first opportunity you get to sell searchers on your webpage, your meta description is your second and equally important opportunity to convince them to take that all-valuable action – clicking through to your website.
Your meta description is the text that is included below your meta title on search results.
This offers you more space (typically 155-160 characters) to further describe and sell the content of that webpage.
Just like your meta title, your meta description is an HTML element that is usually found in the <head> section.
Again, this means you will not be able to see the meta description on the webpage once you have clicked through.
The meta description code will typically look like this:
<head>
<meta name="description" content="Here is an example of the text you would see in your search engine results page (SERP)">
</head>
“A meta description tag generally informs and interests users with a short, relevant summary of what a particular page is about. They are like a pitch that convince the user that the page is exactly what they’re looking for.”
So, it is clear to see why meta descriptions are important. They are a smart way to better engage searchers from within the SERP.
NOTE: Search engines like Google will only use your meta description if they believe it more accurately describes the webpage.
They also don’t use your meta description to determine ranking (but this doesn’t mean it isn’t important).
Meta Descriptions Best Practices
Want to write better meta descriptions? Here are some tips:
Do…
- Keep your descriptions around 155 – 160 characters long
- Create a unique meta description for every page you create
- Include highly relevant information about the content of the page it links to
- Automate meta descriptions for sites with high volumes of content such as news sites
- Include keywords where natural to do so
Don’t…
- Simply list keywords
- Use the same meta description for every page
- Refer to just one element of the page content
- Use very short descriptions
- Exceed 160 characters
Meta Robots
Meta robots might sound like a bad, Silicon Valley-based techno band – but they are actually a very helpful meta tag that is going to help you control what search engines do with your website.
It does this in two ways:
- Telling search engines which web pages on your site to index (show up on SERPs)
- Telling search engines which links on your website to follow
“The robots meta tag lets you utilize a granular, page-specific approach to controlling how an individual page should be indexed and served to users in Google Search results.”
Why does this matter?
Well, when you have a lot of pages on your website, Google can struggle to tell which ones are important and which aren’t.
This means they give all pages the same ‘search juice’.
This is problematic, as it is likely that you want some pages to show up high on SERPs and some to not appear at all.
For example, you may want your latest blog post to show up right at the top of search results, but have no desire for your T&Cs page to appear.
By using the term ‘index’ or ‘noindex’ you tell the search engine whether you want that page to appear or not.
Equally, links on your website to other websites need to be carefully considered. Each link takes a little ‘search juice’ from your site and gives it to the website you are linking to.
This is because a link from your site to another site is a vote of confidence – you are basically saying ‘this content is great and I trust it’.
Of course, this isn’t always bad, but can be especially problematic when you are linking to a site that is trying to rank for the same search terms.
By using the terms ‘follow’ or ‘nofollow’, you tell search engines whether they should follow or ignore links on that page.
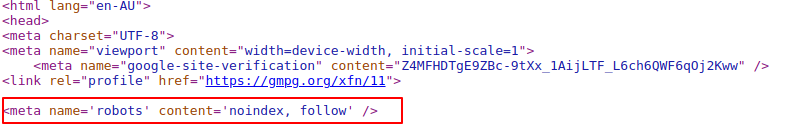
These tags are typically included in the <head> of the website, so would look like this:
- <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex, nofollow”>
- <meta name=”robots” content=”index, follow”>
- <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex, follow”>
- <meta name=”robots” content=”index, nofollow”>
Note: There are some more meta robot commands, but the 4 above are the most commonly used when it comes to SEO.
Meta Robots Best Practices
- Carefully consider which pages you want to rank on search engines and which you don’t
- Only use links on your website which are relevant, high value, and trustworthy – use the ‘nofollow’ tag when you link to pages that aren’t high value or that are competing with your own content
Meta Refresh Direct
The meta refresh direct tag simply redirects a website viewer after a set amount of time. Although this seems a little strange, it is likely that you have come across this on pages that redirect you after an action has been taken.
A familiar message on one of these pages would read a little something like:
“Click here if this page doesn’t refresh in 10 seconds…”
If a refresh direct meta tag is used on a website, it will look like this:
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="4;url="https://examplewebsite.com/">
Why are meta refresh direct pages important to SEO?
Well…they aren’t.
In fact, SEO best practices dictate meta redirect should typically be avoided wherever possible. This is for several reasons, such as:
- It creates a bad user experience, often confusing those on the page and making usual browser functionality (such as the back button) obsolete
- It is often used by websites trying to trick search engines into providing linked pages with more ‘link juice’ – so its use could lead to your website being marked as spam by those search engines
- They actually pass very little or no ‘link juice’ to the website it is redirecting to
Meta Refresh Direct Best Practices
The advice is simple. When it comes to meta refresh direct, wherever possible:
- Don’t use it
- Replace them with 301 or 302 redirects
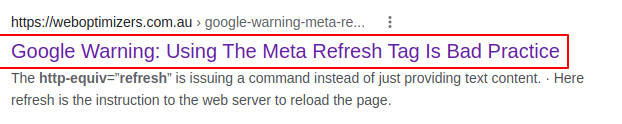
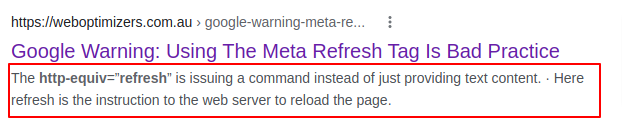
- Google Warning: Using The Meta Refresh Tag Is Bad Practice
- Beginner’s Guide to Google Search Console
Meta Charset
The term ‘charset’ refers to the ‘character set’ of your website.
This meta tag allows webpages to dictate to search engines and browsers how text is transmitted or stored.
It is required because the text on your website is converted to binary – which means it then requires a kind of cipher that will allow characters to be connected to their correct binary equivalents.
If you do not establish a charset, this can lead to the misinterpretation of your content – often this makes it impossible or very difficult to read the text.
Here is what Google has to say about meta charsets:
“This defines the page’s content type and character set. Make sure that you surround the value of the content attribute with quotes – otherwise the charset attribute may be interpreted incorrectly. We recommend using Unicode/UTF-8 where possible.”
There are lots of different character sets. As you can see above, Google recommends using Unicode/UTF-8 on your website.
UTF-8 is the most dominant code used on websites, with 94% of all sites using this code due to the fact that it encodes the most common character, numbers and English with 8-bits. ISO-8859-1 is another popular character set.
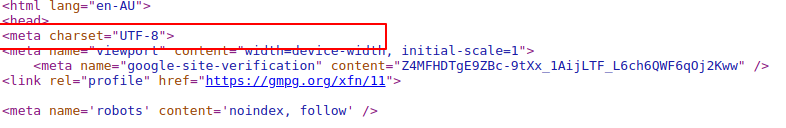
The meta charset on your website will look something like this:
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
Why is meta charset important?
Well, meta charsets aren’t necessarily crucial to SEO success.
Search engines focus on delivering the best content to searchers based on their search terms.
So, doing something like using an alternative charset to UTF-8 isn’t going to directly impact SERP rankings – as browsers can still deliver the correct content.
However, its correct use can have an impact on the usability of your site and therefore impacts your website performance – which, in turn, can impact your SERP rankings.
For example, when your webpages fail to establish the correct charset it can make your page unreadable, tricky to digest, or a hassle to navigate. In turn, this can put other websites off linking through to your content, increase your bounce rate, decrease your session time and make it difficult for search engines to understand what your content is all about – all leading to worse SERP rankings.
Meta Charset Best Practices
- Use UTF-8 (as recommended by Google) where possible
- Ensure you surround the value of the content attribute with quotes (as recommended by Google)
- Include the meta charset tag on all webpages
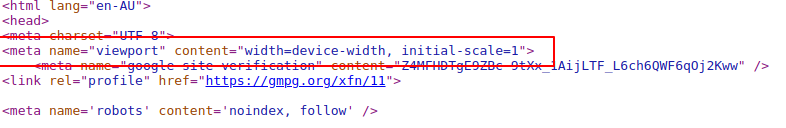
Meta Viewports
Put simply, the viewport is the area of the website you see. So, the viewport when viewing a website on a desktop computer will be bigger than the viewport when viewing the same site on a mobile device.
Meta viewports is an important meta tag, located in the <head> of the HTML, that helps the browser to define exactly which part of the webpage should be visible to visitors.
An incorrect or missing viewport tag will result in a poor user experience, with webpage visitors having to scroll from side to side in order to digest all the content.
Why are viewports important?
It is clear that the incorrect use of viewports can lead to a bad user experience.
This is especially true on mobile devices where webpages typically need to be altered to fit the screen.
When you consider the fact that almost 60% of all global internet traffic is from mobile devices, it is clear how using the correct viewport is essential in making your content digestible by your target audience.
From an SEO point of view, viewports are also very important.
This is due to the fact that mobile-friendly sites are seen as better by search engines and are therefore rewarded by appearing higher in SERPs.
A large part of making your site more mobile-friendly is reducing the amount of time and effort that visitors have to put into navigating your content.
Using a responsive approach to website design is crucial, as visitors could be viewing your site from any device ranging from desktops and laptops to tablets and mobile phones.
So, looking great and being able to easily navigate your site on all these devices is essential to SEO success.
Using meta viewports is the simplest, fastest, and most effective way to boost the mobile-friendliness of your website.
Here is what Google says about sites that don’t use meta viewports:
“For users, this means that font sizes may have an inconsistent appearance, and users may have to double-tap or pinch-to-zoom in order to be able to see and interact with the content.
For Google, we might not judge a page as mobile-friendly because it requires this type of interaction on a mobile device.”
The meta viewport tag will be viewable in your <head> section and will look something like this:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
Meta Viewports Best Practices
Here are some best practices when it comes to using meta viewports on your website:
- Don’t render your webpages to specific widths, as the best width will depend on which device the webpage is being viewed on
- Apply meta viewports to all webpages
- When applying the meta viewport tag, it is best practice to use the “standard” tag
Meta Tags: Summary
Although not all meta tags are crucial to SEO success, it is clear that some tags do have a direct impact on how well your website performs on SERPs.
In the middle ground, there are some tags that don’t necessarily have a direct impact on SEO, but do help you create a website that is more attractive to search engines – so are likely to positively impact your results.
Additional meta tags that Google understands include
- <meta name=”googlebot” content=”…, …”> – this meta tag specifically applies to Googlebot alone unlike robot tag which is for all search engines.
- <meta name=”google” content=”nositelinkssearchbox”> – this meta tag tells Google to not show the search results box in search results.
- <meta name=”googlebot” content=”notranslate”> – When Google recognizes a page in another language, Google will likely provide a translated title and snippet. If you don’t want Google to do this then simply use the meta tag notranslate.’
- <meta name=”google” content=”nopagereadaloud”> – This meta tag prevents Google-text-to-speech services from reading the page our loud.
- <meta name=”rating” content=”adult”> – labels the page as containing adult content so that Google can filter it for SafeSearch results.
Use the tips we have highlighted in this guide to ensure that you are applying the best meta tags to your webpages in the best way possible.
